Artist-friendly parametric modeling tool for 3ds Max
RailClone is the ultimate parametric modeling and assembly tool, with an extensive library and unmatched flexibility and simplicity for creating parametric assets to simplify scene construction. Its unique approach allows you to build sophisticated structures simply by creating visual rules, saving hours of manual work.
24Studio
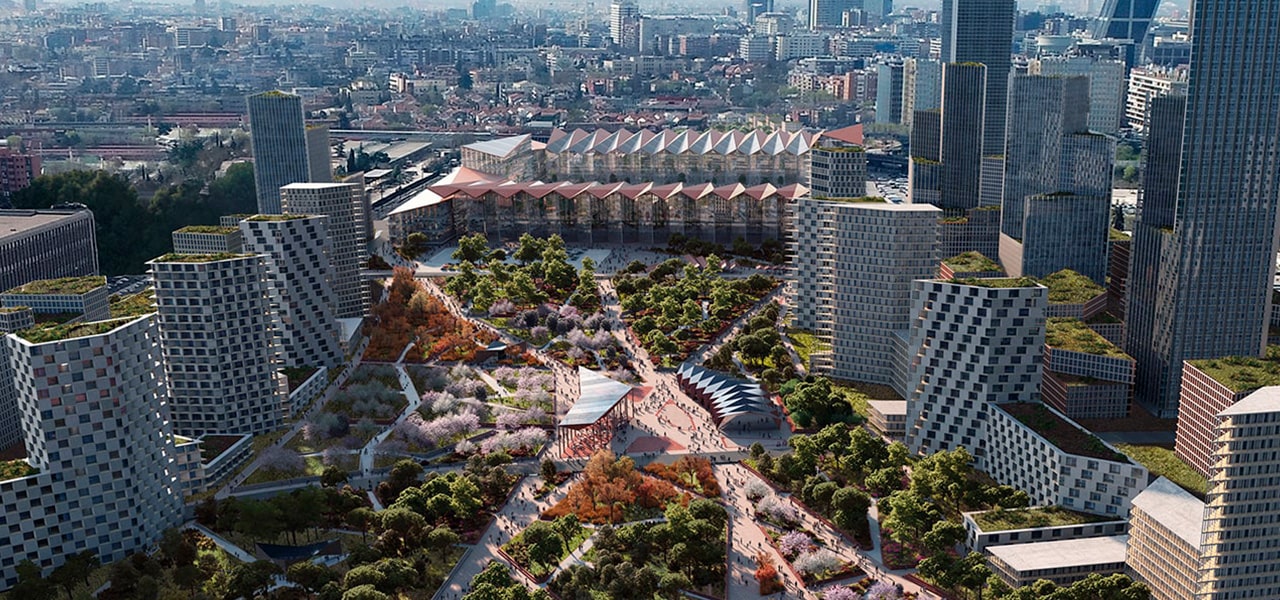

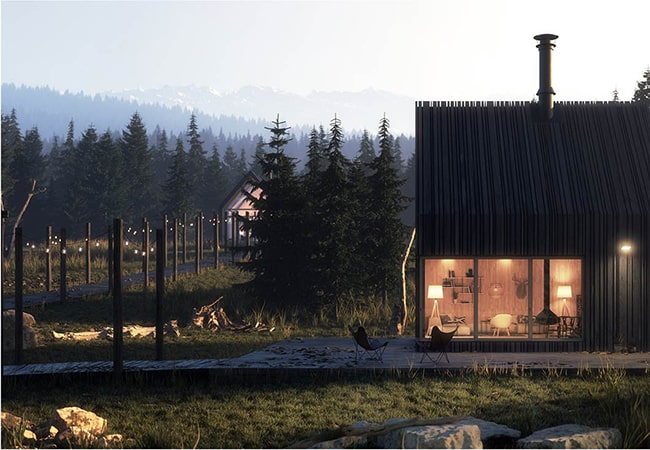
Beauty and the Bit
Overview
Are you tired of losing hours manually updating your scenes after the latest round of client notes? Would you like a faster, easier way to create parametric objects that are flexible, reusable, and easy to update? Introducing RailClone – the powerful artist-friendly parametric modeling plugin for 3ds Max.
Using RailClone, you can build everything from detailed architectural components to cinematic worlds using a simple visual rule-based workflow. Whether you're starting out with the free library, or an advanced user creating your own custom assets, RailClone offers a fast, and efficient way to create smart parametric assets for everyone.
RailClone comes in 2 versions
Try the free Lite version, or go Pro for the full experience
License
Free
What's included?
- RailClone plugin plus RC Slice, and RC Spline modifiers, compatible with 3ds Max (check compatibility information here) with some feature limitations.
- Native support for most popular render engines.
- Library browser with a sample library presets.
Perpetual license
$275
Single payment
What's included?
- RailClone plugin plus RC Slice, and RC Spline modifiers, compatible with 3ds Max (check compatibility information here) with NO limitations.
- Native support for most popular rendering engines.
- Library browser with an expanding library of nearly 500 presets plus the ability to add and manage your own collections.
- Includes RailClone Tools to convert to native instances.
- Includes a one year extendable Maintenance Plan with prioritized technical support, early access to beta versions, and regular updates.
- Perpetual License.
What can you do with RailClone?
From basic architectural elements, to sophisticated scene assembly, Applications for RailClone are almost limitless!
chevron_left
chevron_right
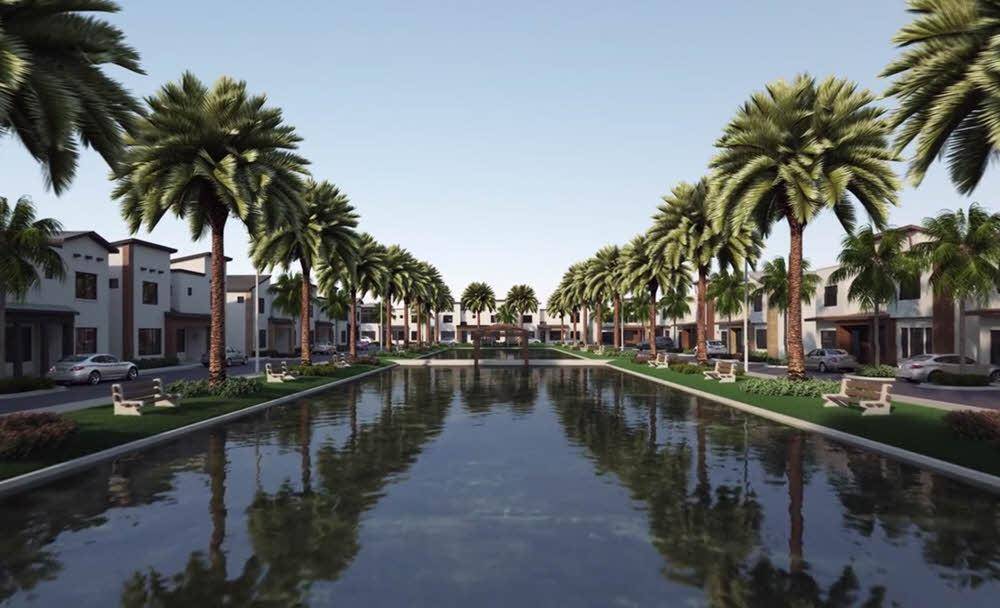
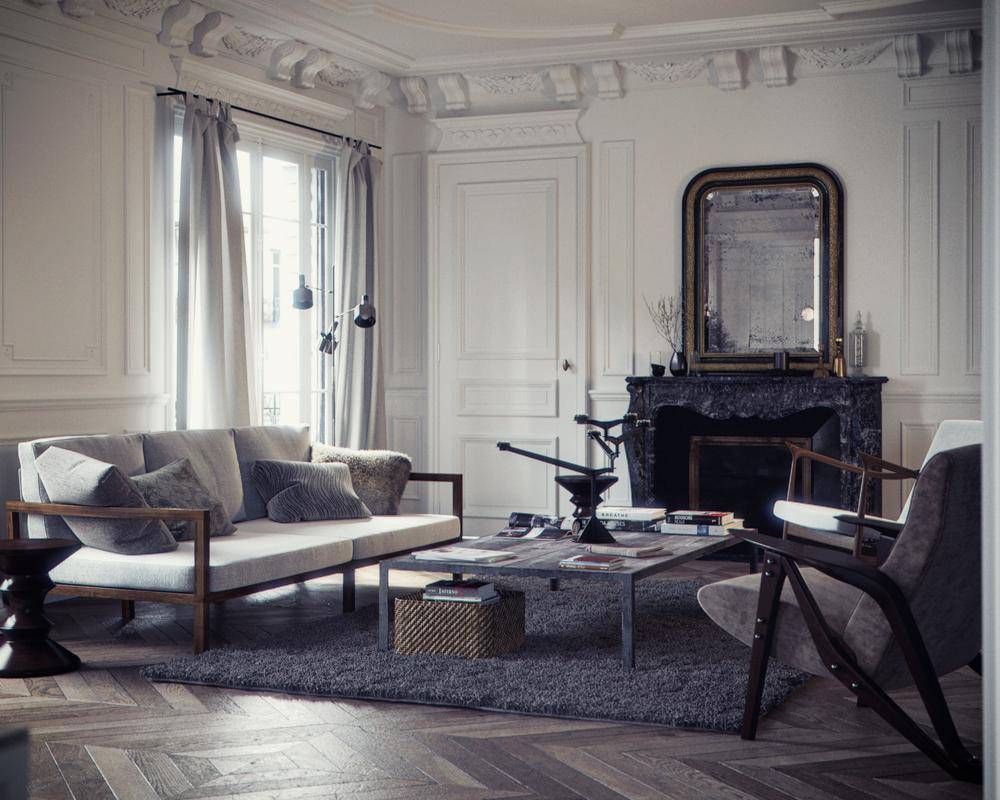
Interior design
RailClone is your essential tool for creating interior environments in architecture, VFX, and games. Whether it's the floor, ceiling or everything in between, it offers hundreds of ways to help you model and design beautiful spaces.
Furniture and shelving
Create customizable furniture and shelving that can be customized to any interior using RailClone's intuitive layout tools.
Moldings
Add detailed skirting, coving, dados, architraves and other types of moldings and trim work to your scenes that adjust to room dimensions.
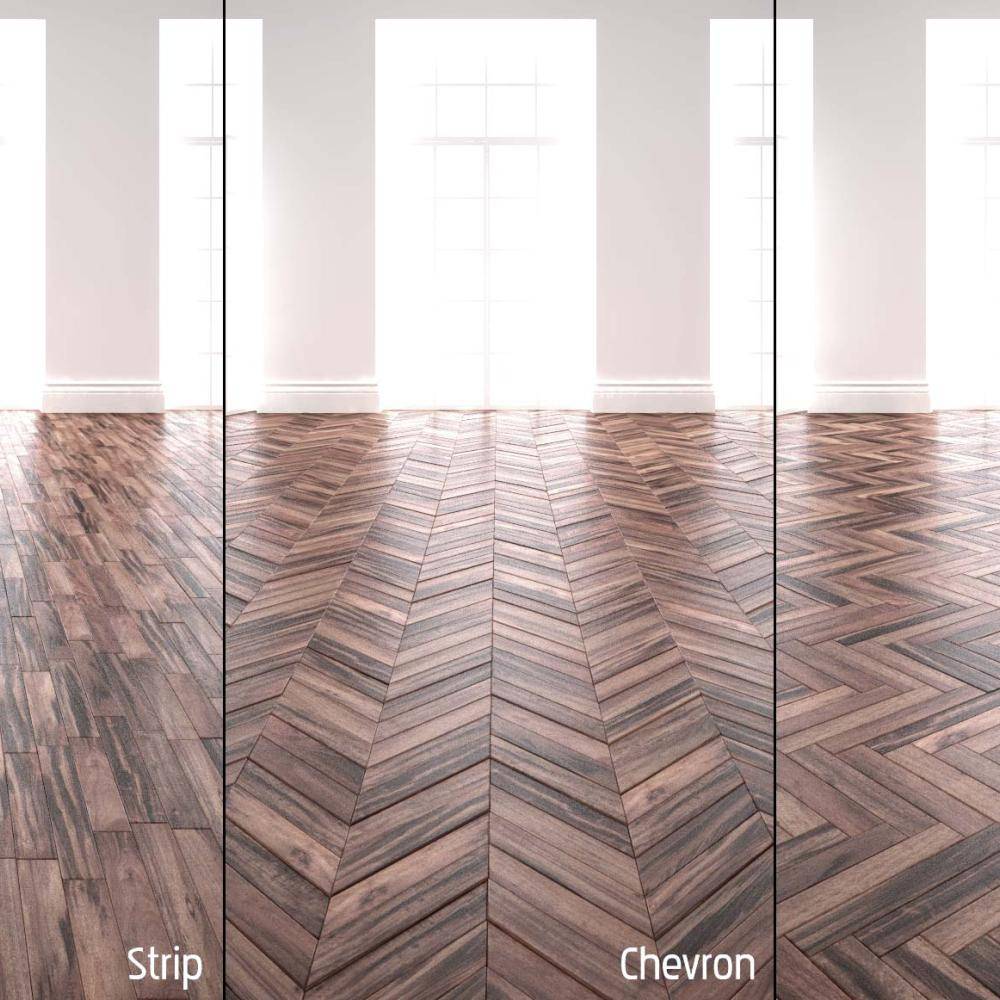
Floors
Automatically fill rooms with parquet flooring just by clicking on the boundary spline and randomize materials for a realistic look!
Stairs and Handrails
Automate the creation of staircases, railings, and handrails, adjusting steps, risers, stringers, and rail height - even for spiral stairs!
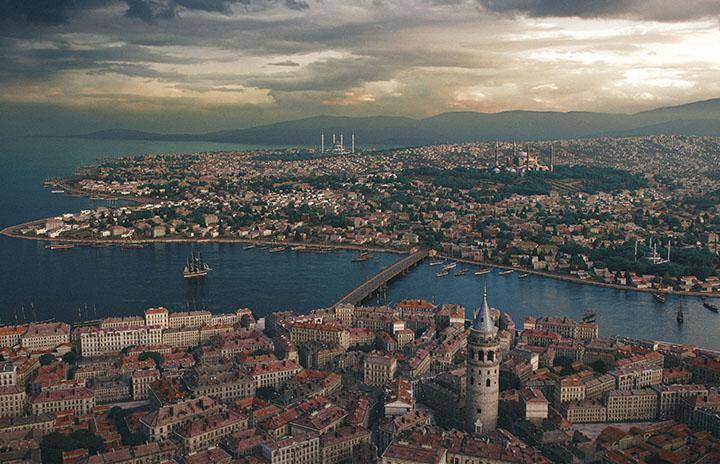
Architecture
Modeling the basic structure of buildings is easy; it's the details that take the time. Let RailClone save you hours of tedious work by automating the modeling and placement of common architectural elements.
Roofs
Generate detailed tiled and slate roofs that seamlessly conform to your architectural plans using RailClone's presets. Complete the look by adding gutters, hips, and ridges for a realistic render.
Windows and Doors
Place windows with ease. RailClone allows for the quick adjustment of window sizes, types, and positions. Perfect for architectural visualizations!
Gutters
Easily generate gutters along the perimeter of roofs. RailClone saves time performing these repetitive but essential tasks for better renders of residential projects.
Facade Systems
Model complex façade systems, including curtain walls, spider glazing, and more, all of which can adapt to any building size.
Mechanical, Electrical, And Plumbing
Model mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems with RailClone's powerful deformation tools. Whether it's routing ductwork, placing electrical sockets, or positioning HVAC, RailClone allows you to quickly adapt to changes in building design.
Ducting and Air Conditioning
Create ducting that adapts to complex layouts, saving time creating detailed HVAC systems for architectural or industrial renders.
Electrical
Simplify the layout of common electrical components such as pylons, sockets, lights, cable trays, switches and more using splines and the RC Spline modifier.

Ambrozie Pura
Water, Oil, and Gas
Model pipes and fittings along splines, including water and gas systems for residential, commercial, or industrial buildings.
Solar and Wind Systems
Visualize renewable energy systems such as solar panels on roofs, photovoltaic power stations, and wind turbines.
Public Utilities
Add public utility infrastructure to your scenes, from street lighting and signage to communications and electrical grids.
Building Elements
When a simple textured plane isn't enough to represent a wall, ceiling, or floor, RailClone has you covered. Create these elements using real geometry in seconds, thanks to the plugin's modular modeling approach
Brick Walls
Build detailed brick walls from real geometry in a variety of bonds and patterns. Use the built in presets or use the rule-based workflow to create your own!
Flooring, Tiles and Mosaics
Create floors from a closed spline with a choice of several customizable patterns and materials, or create your own designs, and even mosaics using RailClone Color.
Cladding
Quickly add cladding to building façades with RailClone. Easily randomize materials and create various patterns to suit many architectural styles.
Ceilings
Add ceiling drop ceilings plus many other styles with the ability to add parameters to adjust styles and layouts with RailClone's parametric tools.
Lights
Arrange lighting systems using rules to customize the position, type, and configurations of lights from simple layouts to large-scale installations.
Access
Modeling access elements like stairs, elevators, and escalators can be tricky and time-consuming to model manually. With RailClone's procedural power, you can quickly create these objects and add customizable attributes, making them easy to reuse in future projects.
Stairs
Create stairs with adjustable dimensions and configurations, from straight to spiral staircases, all in just a few clicks.
Elevators
Add elevators with ease. Using RailClone's tools, users have created fully customizable elevator systems, with adjusting dimensions, doors, and interior details.
Escalators and Travelators
Model elevators that can adapt to any angle and length with several options for materials and types.
Scaffolding
Add access to the exterior of buildings. Use the scaffolding presets from the RailClone library or create your own custom fire escape assets.
Boardwalks
Create boardwalks that snake through your exterior renders of natural landscapes, waterfronts, or urban parks with minimal effort.
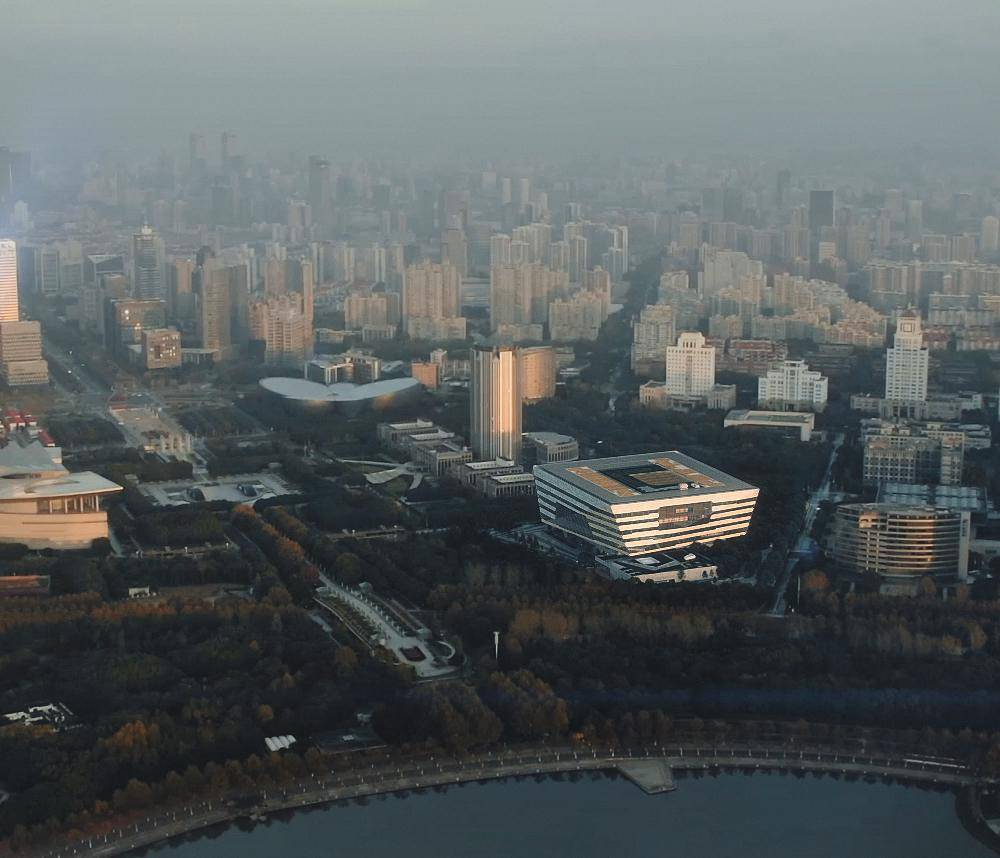
Buildings
Why spend time modeling individual building elements when you could be modeling entire buildings? RailClone is perfect for populating scenes with procedural structures that can easily adapt to any footprint. Ideal for filling the background of your renders.
Residential
Use RailClone to create parametric residential buildings with walls, windows, roofs, and more that automatically adjust to building plans.
Industrial
Quickly generate industrial buildings, or even entire commercial parks, complete with roofs, parking bays, surrounding infrastructure, and much more.
Tower
All it takes is a click on a closed spline to create towers and skyscrapers with RailClone and ParamtricLibraries' building libraries.

Robert Dukes
Warehouses and Commercial
Create warehouse structures with parametric roof, wall, and floor layouts, simplifying large-scale projects that typically already use modular parts.
Commercial
Design commercial and retail spaces including storefronts, shelving, displays, and much more.
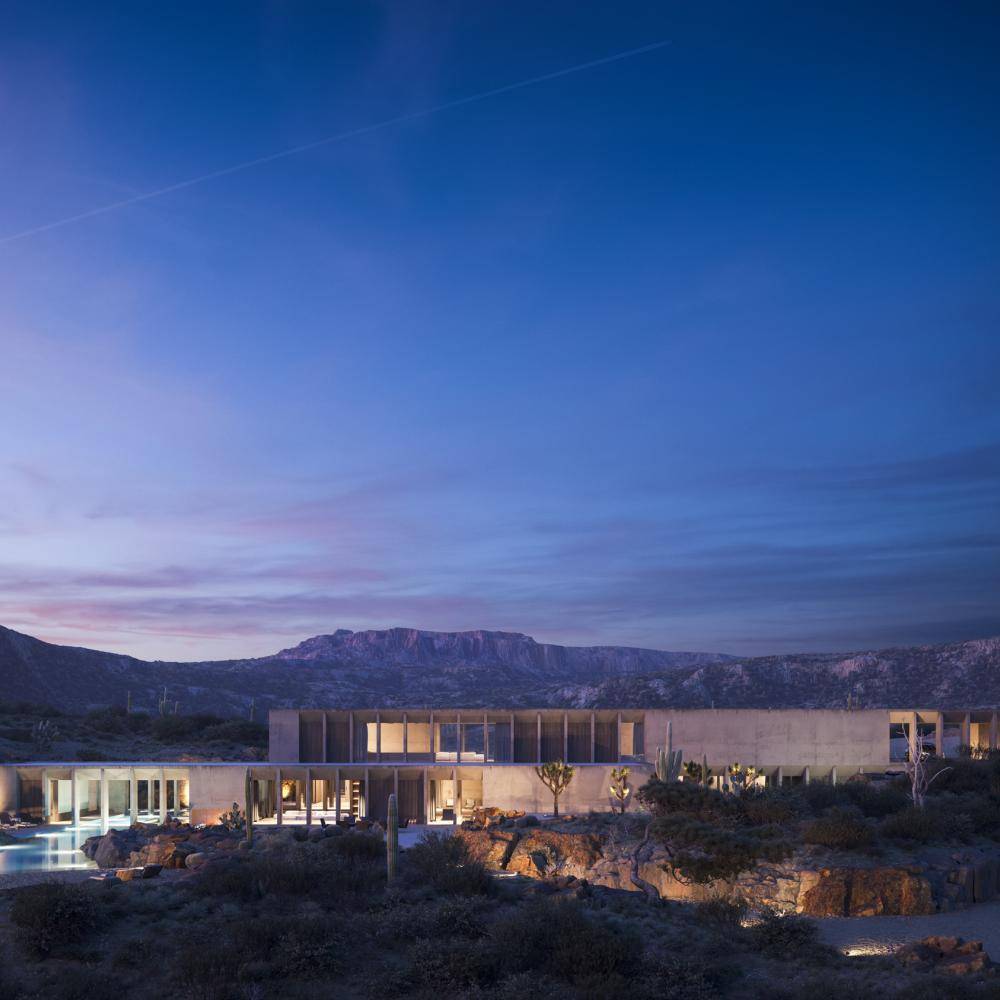
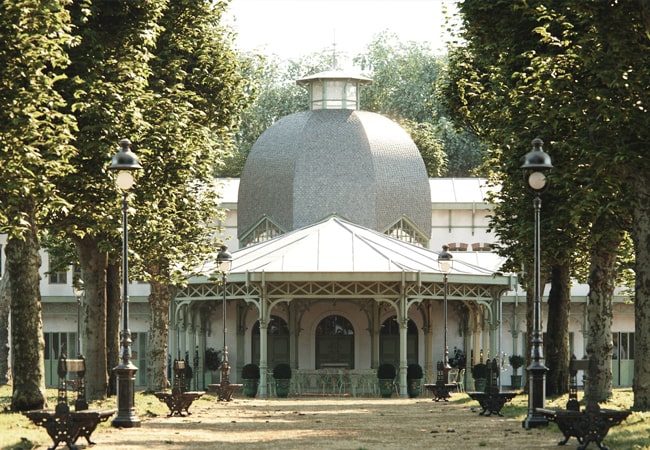
Specialized And Civic Spaces
Model a wide range of public and civic spaces. Whether it's laying out parks, airports, stadiums, or leisure facilities, you can quickly create custom environments using adaptable assets created with RailClone's parametric tools.
Parks
Lay out pathways, benches, railing and more to create public parks. Combine RailClone with ForestPack to add vegetation for a complete toolkit for environment creation.
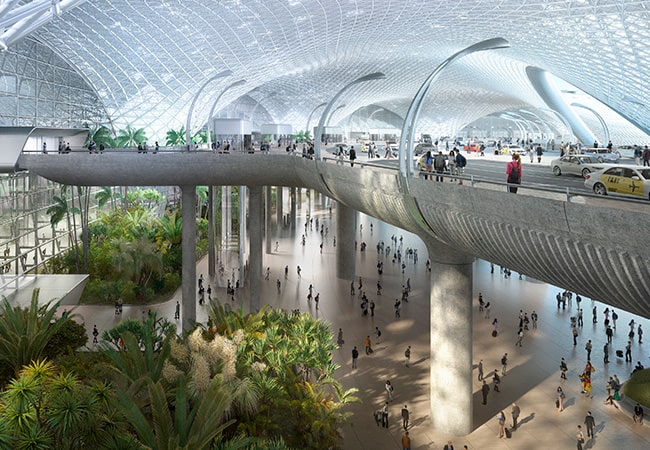
Airports
Easily visualize complex airport layouts. Create customizable conveyors, runways, seating areas, and other props and structural elements.
Stadiums
Automate the creation of stadium seating, roofing, lights, parking, and other infrastructure, ideal for large-scale sports venues.
Leisure Facilities
Design leisure centers, pools, play parks, and other public spaces using easy to edit assets.
Libraries
Render impressive library spaces with easy to customize shelving complete with books, plus tables, chairs and much more.
Roads, Civil Engineering, And Infrastructures
Quickly lay out urban infrastructure, from roads, barriers, markings, and signage to bridges, pavements, curbs, and street furniture. Drive it all from a handful of splines to make updates a cinch!
Roads, Markings, Signs and Lights
Lay out roads, highways, and add road markings, signs, and street lights with RailClone's flexible spline-based tools, which can even follow undulating terrains.
Pavements and Curbs
Create pavements, curbs, and more adapting to the design of urban spaces with minimal effort.
Street Furniture
Easily place street furniture like benches, lights, and bins using RailClone's easy-to-use parametric library.
Bridges
Create many types of bridges with customizable parametric elements for roads, barriers, and structural supports.
Railways
Create railway tracks that can follow a terrain to seamlessly integrate with surrounding landscapes.
How does it work?
Creating parametric models has never been simpler!

ITOOSOFT
widgets
Choose your geometry
RailClone simplifies complex modeling by using a “building block” approach. Instead of creating objects from scratch, you start with small, reusable pieces of geometry called segments. These segments are like LEGO® bricks that RailClone can arrange and multiply to build larger, more sophisticated forms.

ITOOSOFT
show_chart
Pick a spline
RailClone uses Splines to guide the placement of your segments. These splines define the path along which the segments, such as architectural elements or building components, are distributed. Using RailClone can be as simple as loading a preset from the free library and picking a spline.

ITOOSOFT
design_services
Set the rules
Once your segments and spline are in place, RailClone uses a set of instructions to determine how geometry is assembled along the path. You can either use a preset or create your own rules using the simple node-based editor. Adjustments are instantly visible in the viewport, enabling real-time feedback and a fast iterative workflow.
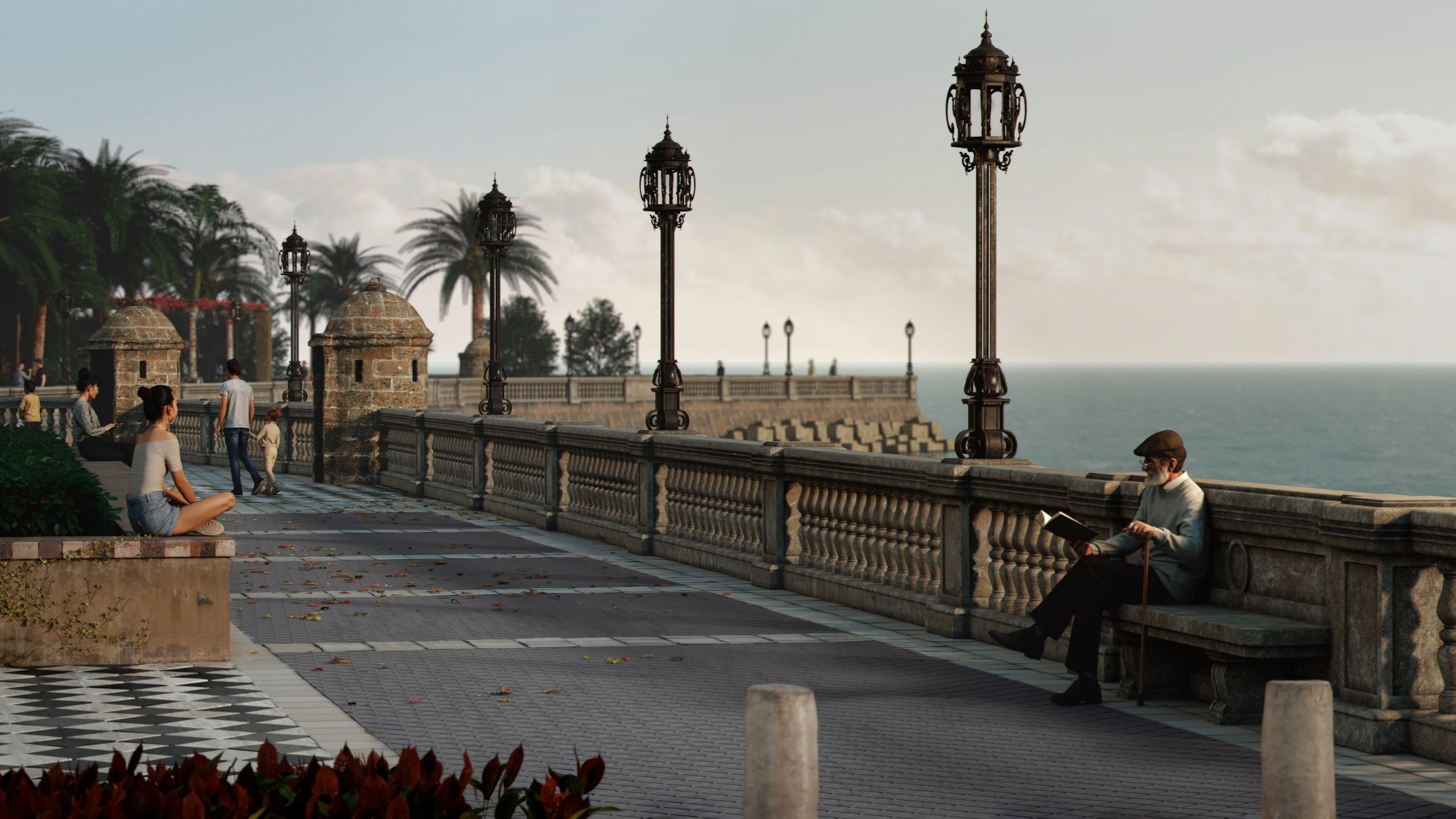

ITOOSOFT
What's new?
See what's new in the latest release of RailClone

AVEO Studios
Spline Boolean
A new Boolean operator allows you to combine, subtract, intersect, or exclude spline regions, providing new ways to generate complex layouts procedurally.
Spline Offset
Create multiple offset copies of a spline while controlling their spacing, rotation, and translation. Choose between 2D and 3D modes for flexible alignment and auto-heal intersections.
Catenary Curves
A new Catenary operator allows you to generate hanging cables, chains, and other suspended structures. Adjust absolute and relative drop values to create realistic sagging curves.
Divide Splines
The new Divide operators allow you to subdivide splines at even intervals or by markers, while the Connect node automatically links separate splines using straight-lines.
Connect Splines
The Connect operator generates straight paths between two splines. Ideal for structural designs like bridges, and anything else that needs networks of adaptable connected elements.
Conform Splines to Surfaces
Project splines onto terrain and other surfaces while retaining full procedural control, making it easier to create paths, fences, and other elements on uneven ground.
New Shape Primitives
Generate standard spline shapes such as lines, rectangles, and circles directly inside the RailClone Style Editor. This eliminates the need to create separate splines in 3ds Max.
More Flexible Macros
Macros now support multiple outputs, allowing a single macro to pass multiple segment, numeric, or spline properties. This makes it easier to create complex parametric models with fewer nodes.
Faster Point-Cloud Display
A major optimization to the point-cloud system improves viewport performance. Enjoy smoother interaction and reduced GPU redraw times when working with large RailClone objects.
ITOOSOFT
Introducing RailClone Systems!
Smart, parametric assets that make procedural modeling more accessible than ever. RailClone Systems allow you to customize flexible, adaptive models in 3ds Max with ease. No need to start from scratch, with RailClone Systems the power of RailClone is just a few clicks away.
Discover RailClone Systems!Compatibility
Works with 3ds Max and most popular rendering engines
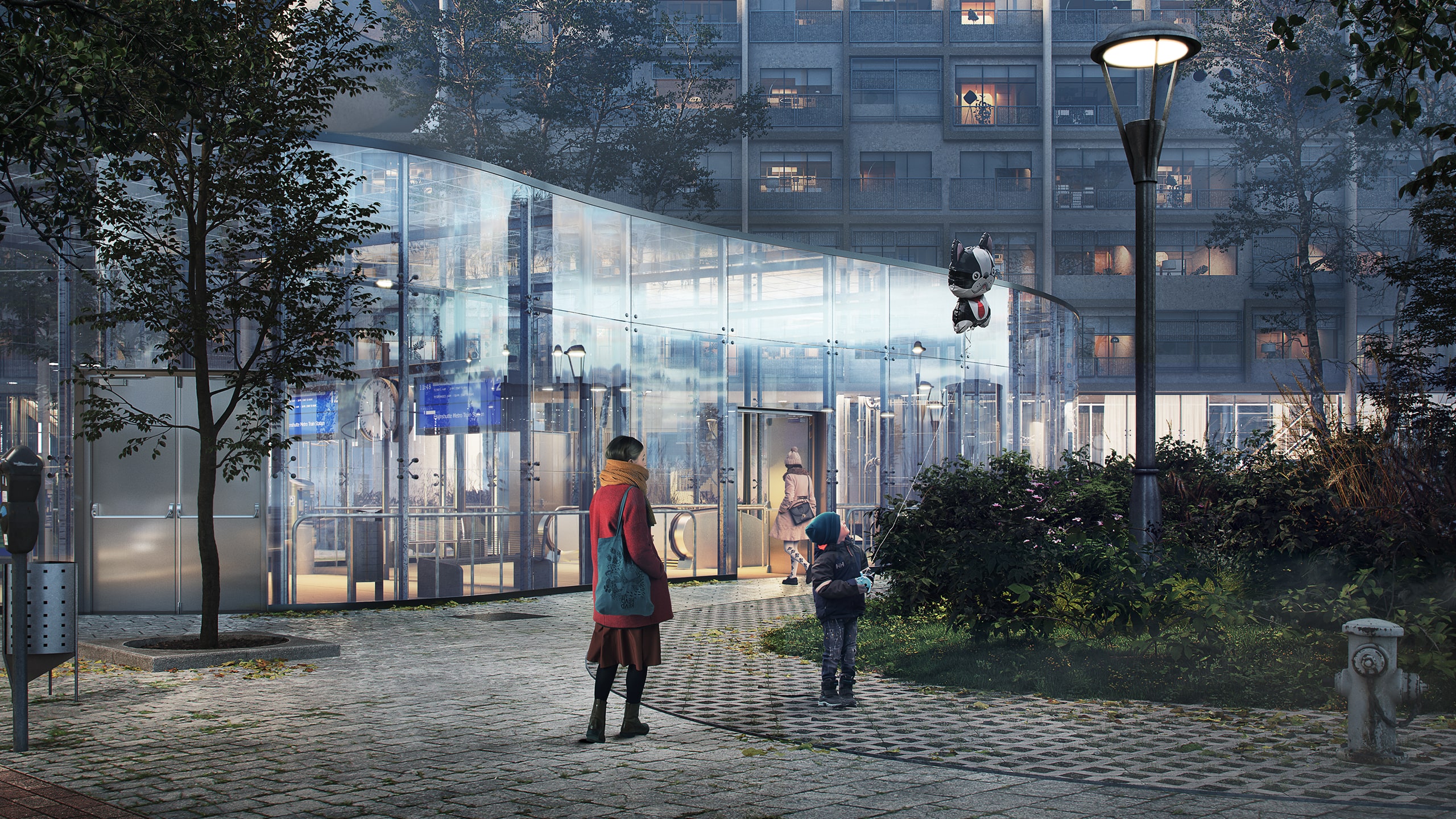

RZGraphics
Free library of nearly 500 assets
Hundreds of ready-to-use fully procedural assets including curtain walls, cladding, roofs, railings, guttering, walls, escalators, flooring, roads, street lights, pavements, ducting, parking, fences, and much more!














Get inspired
See what's possible when unbeatable tools meets amazing artists
What our users are saying
Why industry experts depend on our software

Get up and running fast with detailed tutorials
We value our customers and want them to get the best out of our plugins. That's why we offer an unbeatable library of tutorials to help you learn, maximize the potential of, and seamlessly integrate your new purchases into your pipeline.
Try / Buy
Join thousands of satisfied RailClone users
License
Free
What's included?
- RailClone plugin plus RC Slice, and RC Spline modifiers, compatible with 3ds Max (check compatibility information here) with some feature limitations.
- Native support for most popular render engines.
- Library browser with a sample library presets.
Perpetual license
$275
Single payment
What's included?
- RailClone plugin plus RC Slice, and RC Spline modifiers, compatible with 3ds Max (check compatibility information here) with NO limitations.
- Native support for most popular rendering engines.
- Library browser with an expanding library of nearly 500 presets plus the ability to add and manage your own collections.
- Includes RailClone Tools to convert to native instances.
- Includes a one year extendable Maintenance Plan with prioritized technical support, early access to beta versions, and regular updates.
- Perpetual License.
add
Perpetual license
$550$499
Single payment
Rashed Abdullah
An exclusive range of high-quality ready-to-use RailClone Pro assets, only available from ITOOSOFT.
PPG Studio
FAQ
Answers to common questions
chevron_left
chevron_right
Can I sell assets made using RailClone?
Yes. We place no restrictions on selling assets made with RailClone as long as the models and textures used do not originate from our built-in libraries.
Can I create my own assets or use them from other vendors in addition to the RailClone library?
Of course! RailClone is an authoring tool that can be used to create your own assets by adapting presets or entirely from scratch. There are also vendors that provide additional 3rd party libraries.
Is there a feature compatibility list I can use to check if my renderer is supported?
You can see a list of all the features and whether they are supported by a renderer in our documentation
Can I use RailClone Lite for my commercial projects?
Yes. Both plugins can be used for personal or commercial projects.
What are the license restrictions for the library models and sample scenes?
You can use the samples and library models for your own scenes, but you are not authorized to distribute or resell any model based entirely or partially on them, including geometry, texture or materials. This limitation applies both for the Lite and Pro products
How does the activation process work?
With an active Internet connection, the activation process can be completed online. The software will connect with our activation server through a secure connection, and the activation codes will be sent and installed automatically. If your computer is not connected to the Internet, there are alternative activation methods using a web page or by email
How many times can I activate a license?
For security reasons, our activation server allows you to activate a license only a certain number of times (5 by default). If you exhaust the maximum number of activations, please message us using the contact form and we will increase the activation counter associated with your license.
Can I transfer the license to another computer?
Actually, the software doesn't include any option to transfer the license. To move the software to another computer, uninstall it from the old machine and activate the license on the new one. For this purpose we allow 5 activations by default with each license, which should be enough for a long time, and you can request additional activations when needed. If you change your computer frequently, we suggest purchasing a network license type (see details below).
What is the difference between standalone and network licenses?
Under a standalone license, the software is constrained to a certain host. A license is needed for each computer the software will be installed on.
In network license mode, a pool of licenses is available on the server, for use in any computer on the network. You only need to have licenses for the maximum number of simultaneous users expected, not for each computer where the software will be installed. Network licenses cost the same as standalone licenses.
A great advantage of the network licenses is that you only need to install and activate licenses on the server, not on the workstations. This allows you to change or upgrade the computers more easily, without having to worry about reactivating licenses.
In network license mode, a pool of licenses is available on the server, for use in any computer on the network. You only need to have licenses for the maximum number of simultaneous users expected, not for each computer where the software will be installed. Network licenses cost the same as standalone licenses.
A great advantage of the network licenses is that you only need to install and activate licenses on the server, not on the workstations. This allows you to change or upgrade the computers more easily, without having to worry about reactivating licenses.
What are the requirements to use network licenses?
Network licenses require you to install the License Server software in a Windows computer. It may be a workstation (even the same machine used to run Max), or a separate server.
Although the server software does not require a powerful system, it is mandatory that the computer hosting the license server be running and available while there are computers using the licensed software.
Although the server software does not require a powerful system, it is mandatory that the computer hosting the license server be running and available while there are computers using the licensed software.
Do I need to purchase additional licenses for my render nodes?
No. In the setup program you will find a specific installation option for render nodes. There is no limit to how many nodes you can install and they are free as long as you are not a commercial rendering farm.
Can I edit scenes on one workstation while rendering on another with a single license?
One license is required for each workstation to edit or render interactively. We define interactively as using 3ds Max manually by an operator.
Non-interactive render modes (such as batch render, distributed rendering or backburner) don't require any license.
Non-interactive render modes (such as batch render, distributed rendering or backburner) don't require any license.
Can I open scenes which use the plugin on computers that don't have an active license?
Yes. You can open and work with the scenes, but the objects cannot be edited or rendered.
Who will process my order?
Your order will be securely processed through our partner 2CO. You will be redirected to a part of their website dedicated to ITOOSOFT.
How do I know the status of my order?
Once you have finished the checkout process and entered payment details, your order will be processed automatically, normally within minutes (on rare occasions, it may take a little longer). Once completed, you will be notified via email with instructions on how to download and install the software.
How can I get an invoice for my purchase?
After completing the order, you will receive an invoice from 2CO, with the confirmation email.
Is VAT included in the prices shown above?
The prices shown on the web don't include VAT.
Value Added Tax (VAT, IVA, TVA, MwSt, BTW). For European Customers Only.
In some cases, a percentage of VAT will be added to the product price, depending on where you live and if you're ordering for a company or for personal use.
The final selling price will be displayed after entering all the customer's data and before the order is completed.
If you are a business customer within the European Union, be sure to enter your VAT ID in the order form, to correctly calculate the VAT percentage.
Value Added Tax (VAT, IVA, TVA, MwSt, BTW). For European Customers Only.
In some cases, a percentage of VAT will be added to the product price, depending on where you live and if you're ordering for a company or for personal use.
The final selling price will be displayed after entering all the customer's data and before the order is completed.
If you are a business customer within the European Union, be sure to enter your VAT ID in the order form, to correctly calculate the VAT percentage.
What is an Upgrade Maintenance Plan?
The Maintenance Plan gives you access to the following benefits.
Automatic upgrades to the most up-to-date versions of the software, including major releases and patches.
Early access to Beta versions and the opportunity to test and suggest new features before they are included in the final release.
Premium technical support and prioritized incident management, including first response to your issues within 1 business day, and usually much faster than that.
Special subscriber-only promotions and discounts.
By default, all licenses include a one-year maintenance, but you can choose an extended plan at the time of purchase.
Automatic upgrades to the most up-to-date versions of the software, including major releases and patches.
Early access to Beta versions and the opportunity to test and suggest new features before they are included in the final release.
Premium technical support and prioritized incident management, including first response to your issues within 1 business day, and usually much faster than that.
Special subscriber-only promotions and discounts.
By default, all licenses include a one-year maintenance, but you can choose an extended plan at the time of purchase.
What happens when the maintenance plan period expires? Does the software stop working?
Absolutely not. You can continue using the product forever. Once your maintenance plan expires, you will not be able to download the latest upgrades.
What are the benefits of choosing a three-year maintenance plan?
When you purchase a license of our products, you receive a one-year maintenance plan by default. The three-year maintenance plan guarantees a long period of software updates and new features, with a discount.